1. 慢查询SQL优化思路
1.1 优化什么样的SQL?
优化是有成本的, 首先选择给系统带来最大收益的sql
10000次20次io/h; 10次20000次io/h
优化哪个? 优化考虑高并发的SQL;
1.2 确定优化对象的性能瓶颈是CPU还是IO?
数据访问耗时太多?–>有无索引?是不是没索引,走的全表搜啊秒? 需不需要建索引?
是CPU的瓶颈? –> 分组/排序是不是有问题?
1.3 优化目标是什么? 优化到什么标准?
硬件的承受范围
业务的承受范围
能够给用户带来的体验
1.4 从explain分析入手
1.5 join中用小集驱动大集(把小结果集放外层)
2个表做join查询, 相当于两个for循环, 外层一个, 内层一个; 把小的结果集放在外层, 这样, 外层循环的次数就小; 比如外层20个记录,内层100万记录, 这样外层循环20次, 每次取一条取匹配100万中符合的数据, 形成的数据集就相对压力小;
但是如果把100万放外层, 相当于至少得100万次循环!
1.6 尽量在索引中完成排序
如果order by 的字段都有索引, 就会用索引来进行排序, 因为索引本身就是有序的;
最好的就是 select的列和order by的列都有索引, 这样用索引就可以完成;
如果order by 的列没有索引, 会从表中把数据取出, 开辟单独内存空间来进行排序, 如果内存空间也不够, 只能借助临时文件进行排序, 甚至可能落盘(写入临时文件-增加物理IO);
1.7 杜绝select*, 只取需要的列
节约网络带宽, select * 有可能不走索引;
但是如果 select 指定列上有索引, 是会走索引的;
1.8 使用最有效的过滤条件
假如where的3个字段都有索引, 选哪个呢?后面续.
1.9 避免复杂的join和子查询
join的表越多, 数据库压力越大, 可以分步结果, 用程序处理, 得到结果;然后二次查;
1.10 小心 order by, group by, distinct语句
需要分组/排序的, 让目标列走索引!
这样就不需要额外的内存空间和临时表
1.11 合理设计并利用索引
2. join的优化
2.1 join中用小集驱动大集(把小结果集放外层)
2.1.1 驱动表
- 指定了连接条件: 满足条件的记录少的表(where过滤后);
- 未指定连接条件: 表中行数少的表;
2.1.2 left-join, right-join, inner-join的区别
join的原理
通过驱动表的结果集作为循环基础数据, 然后一条一条通过该结果集中的数据, 作为过滤条件, 到下一个表查询数据, 最后合并结果;
1). 左连接驱动表就是左表;
左连接驱动表就是左表; 左表数据全部展示, 不属于左表的字段全部NULL展示;
2). 右连接驱动表就是右表
右连接驱动表就是右表; 右表数据全部展示, 不属于右表的字段全部NULL展示;
3). 内连接不指定驱动表, mysql自己选行数少的(一般情况)
内连接只显示交集部分; 内连接不指定驱动表, MySQL自己根据哪个表数据少来作为驱动表; 下面两个等价, 都是内连接:
select * from t1 join t2 on t1.id=t2.id;
select * from t1, t2 where t1.id=t2.id;有一点需要注意: 假如有以下前提:
t1表: id无索引, 有10万条记录;
t2表: id有索引, 有10条记录;
如下:
mysql> desc t1;
+-------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | bigint(20) unsigned | NO | | 0 | |
| name | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| price | double | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*) from t1;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 150000 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.05 sec)
mysql> desc t2;
+-------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | bigint(20) unsigned | NO | PRI | 0 | |
| name | varchar(10) | YES | MUL | NULL | |
| price | double | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*) from t2;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 10 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from t1 join t2 on t1.id=t2.id;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+------+---------+------------+--------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+------+---------+------------+--------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 149692 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | eq_ref | id | id | 8 | test.t1.id | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+------+---------+------------+--------+----------+-------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)从 explain select * from t1 join t2 on t1.id=t2.id; 可以看出 第一条是 t1表, 也就是说, 驱动表是t1表.
这跟上面说的内连接的驱动表由mysql自己选, 选记录少的来做驱动表不符啊!
问题就在索引: MySQL在选驱动表时, 看到 t2 表是有索引的, 所以, 驱动表就选择了没有索引的表–因为驱动表是用来遍历的, 不用索引的功能;
我们看查询的性能:
mysql> select * from t1 join t2 on t1.id=t2.id;
+----+---------+--------+----+---------+--------+
| id | name | price | id | name | price |
+----+---------+--------+----+---------+--------+
| 1 | 商品1 | 200.17 | 1 | 商品1 | 200.17 |
| 2 | 商品2 | 200.87 | 2 | 商品2 | 200.87 |
| 3 | 商品3 | 200.81 | 3 | 商品3 | 200.81 |
| 4 | 商品4 | 200.43 | 4 | 商品4 | 200.43 |
| 5 | 商品5 | 200.73 | 5 | 商品5 | 200.73 |
| 6 | 商品6 | 200.36 | 6 | 商品6 | 200.36 |
| 7 | 商品7 | 200.61 | 7 | 商品7 | 200.61 |
| 8 | 商品8 | 200.98 | 8 | 商品8 | 200.98 |
| 9 | 商品9 | 200.06 | 9 | 商品9 | 200.06 |
| 10 | 商品0 | 200.38 | 10 | 商品0 | 200.38 |
+----+---------+--------+----+---------+--------+
10 rows in set (0.43 sec)查询花费了0.43秒;
4). 自己指定驱动表;
我们可以怎么优化呢? 自己指定驱动表为t2, 用记录少的表来驱动: 改为right join 即可用右表驱动:
mysql> select * from t1 right join t2 on t1.id=t2.id;
+------+---------+--------+----+---------+--------+
| id | name | price | id | name | price |
+------+---------+--------+----+---------+--------+
| 1 | 商品1 | 200.17 | 1 | 商品1 | 200.17 |
| 2 | 商品2 | 200.87 | 2 | 商品2 | 200.87 |
| 3 | 商品3 | 200.81 | 3 | 商品3 | 200.81 |
| 4 | 商品4 | 200.43 | 4 | 商品4 | 200.43 |
| 5 | 商品5 | 200.73 | 5 | 商品5 | 200.73 |
| 6 | 商品6 | 200.36 | 6 | 商品6 | 200.36 |
| 7 | 商品7 | 200.61 | 7 | 商品7 | 200.61 |
| 8 | 商品8 | 200.98 | 8 | 商品8 | 200.98 |
| 9 | 商品9 | 200.06 | 9 | 商品9 | 200.06 |
| 10 | 商品0 | 200.38 | 10 | 商品0 | 200.38 |
+------+---------+--------+----+---------+--------+
10 rows in set (0.27 sec)可见性能得到了提升; 这时候, 如果我们给t1表加上了索引, 性能会进一步提升:
mysql> alter table t1 add unique index(id);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (2.02 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from t1 right join t2 on t1.id=t2.id;
+------+---------+--------+----+---------+--------+
| id | name | price | id | name | price |
+------+---------+--------+----+---------+--------+
| 10 | 商品0 | 200.38 | 10 | 商品0 | 200.38 |
| 1 | 商品1 | 200.17 | 1 | 商品1 | 200.17 |
| 2 | 商品2 | 200.87 | 2 | 商品2 | 200.87 |
| 3 | 商品3 | 200.81 | 3 | 商品3 | 200.81 |
| 4 | 商品4 | 200.43 | 4 | 商品4 | 200.43 |
| 5 | 商品5 | 200.73 | 5 | 商品5 | 200.73 |
| 6 | 商品6 | 200.36 | 6 | 商品6 | 200.36 |
| 7 | 商品7 | 200.61 | 7 | 商品7 | 200.61 |
| 8 | 商品8 | 200.98 | 8 | 商品8 | 200.98 |
| 9 | 商品9 | 200.06 | 9 | 商品9 | 200.06 |
+------+---------+--------+----+---------+--------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)得嘞~~您瞅瞅!! 看下 explain 分析:
mysql> explain select * from t1 right join t2 on t1.id=t2.id;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+--------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+--------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | NULL | name_2 | 42 | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | eq_ref | id | id | 8 | test.t2.id | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+--------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from t1 join t2 on t1.id=t2.id;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+--------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+--------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | id | name_2 | 42 | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | eq_ref | id | id | 8 | test.t2.id | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+--------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)加不加 right , 都使用 t2 表作为驱动表了!!
2.2 MySQL的join算法-Nest-Loop-Join原理
mysql只支持一种join算法: Nested-Loop Join(嵌套循环连接)
但是 它又有3中变种:
1). Simple 嵌套循环连接-简单嵌套循环链接连接
现在已经不会走这种模式了; 会直接选择 块 嵌套循环连接;
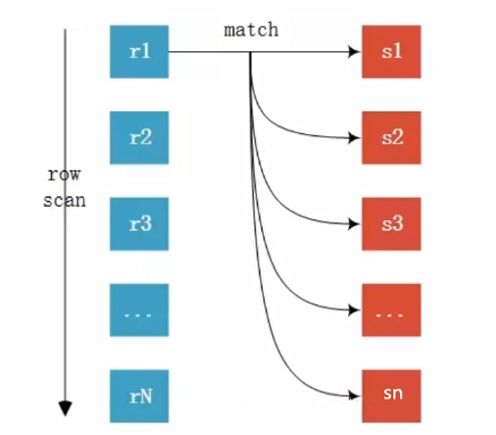
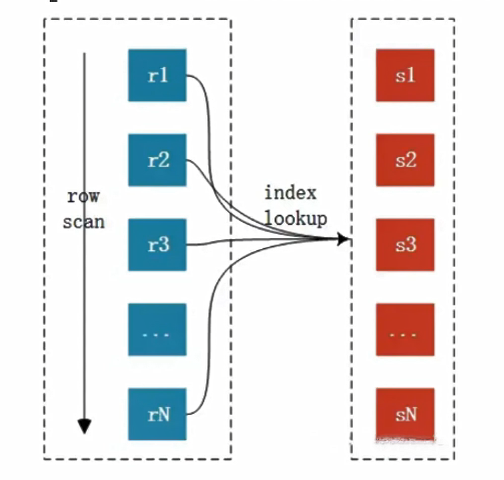
2). Index 嵌套循环连接-索引嵌套循环链接连接
在简单 嵌套循环连接的 基础上, 拿每次第一个表的一行记录, 去第二个表的索引中匹配, 而不是扫表;
3). Block 嵌套循环链接-块嵌套循环链接连接
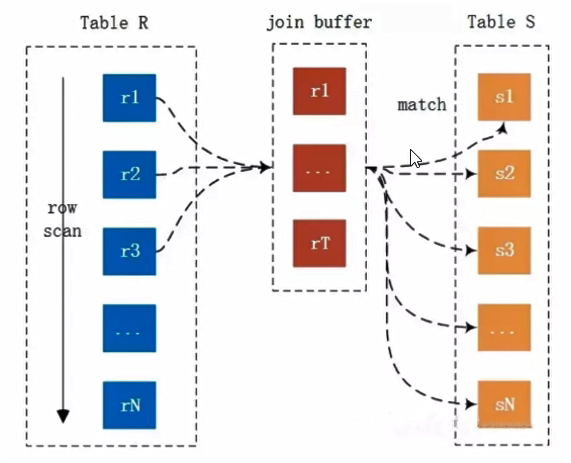
假如上面的t1/t2都没有索引, 这时, mysql也不会使用 简单嵌套循环连接, 而是使用 块嵌套循环连接:
mysql> show index from t1;
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| t1 | 0 | id | 1 | id | A | 149999 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show index from t2;
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| t2 | 0 | id | 1 | id | A | 10 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| t2 | 1 | name | 1 | name | A | 10 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| t2 | 1 | name_2 | 1 | name | A | 10 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| t2 | 1 | name_2 | 2 | price | A | 10 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> drop index id on t1;
Query OK, 150000 rows affected (1.05 sec)
Records: 150000 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> drop index id on t2;
Query OK, 10 rows affected (0.08 sec)
Records: 10 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> explain select * from t1 join t2 on t1.id=t2.id;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 149994 | 10.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop)
说明, 使用了内存 join buffer, 默认大小是 256k;
优化思路:
- 尽可能减少join中的 Nested-Loop 循环总次数;
- 优先优化 Nested Loop的内层循环; (比如索引 嵌套循环连接)
- 在join语句中被驱动表上建立索引; (就是第二条的实际优化方法)
- 在join语句中被驱动表上无法建立索引; 那么在内存充裕的条件下, 充分使用 join buffer的设置;
2.3 Mysql的 inner join的算法选择
t1, t2表特征如下:
mysql> show index from t1;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show index from t2;
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| t2 | 0 | t2 | 1 | id | A | 10 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| t2 | 1 | name | 1 | name | A | 10 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| t2 | 1 | name_2 | 1 | name | A | 10 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| t2 | 1 | name_2 | 2 | price | A | 10 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*) from t1;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 150000 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.05 sec)
mysql> select count(*) from t2;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 10 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)2.3.1 case1-大表无索引, 小表有索引:
t1有15条行数据, 没有索引;
t2有10条数据, id上有索引;
- 如果join不指定连接条件:
mysql> explain select * from t1 join t2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+--------+---------+------+--------+----------+---------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+--------+---------+------+--------+----------+---------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | NULL | name_2 | 42 | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 149994 | 100.00 | Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+--------+---------+------+--------+----------+---------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)mysql会选用 块 嵌套循环连接; 如果指定了 连接条件呢?
mysql会选用无索引表, 作为驱动表, 索引表作为内层循环, 请看:
mysql> explain select * from t1 join t2 on t1.id=t2.id;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+------+---------+------------+--------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+------+---------+------------+--------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 149994 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | eq_ref | t2 | t2 | 8 | test.t1.id | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+------+---------+------------+--------+----------+-------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)2.3.2 case2-大表无索引, 小表无索引:
我们把小标t2的id的索引删掉再看:
mysql> alter table t2 drop index t2;
Query OK, 10 rows affected (0.08 sec)
Records: 10 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> show index from t2;
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| t2 | 1 | name | 1 | name | A | 10 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| t2 | 1 | name_2 | 1 | name | A | 10 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| t2 | 1 | name_2 | 2 | price | A | 10 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)此时 t2.id 已无索引, 再看看, mysql是怎么选择 Nested-Loop Join的算法的:
mysql> explain select * from t1 join t2 on t1.id=t2.id;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 149994 | 10.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)可以看到: 第一个步骤又是 t2 表了, mysql “聪明地” 选择了小标作为驱动表, 在内层嵌套循环连接时, “机智的”使用了 (Block Nested Loop), 我们看到, Block 循环嵌套连接, 使用了 join buffer;
2.4 Nest Loop Join算法小结
事实上, Simple Nested-Loop Join已经不会使用了, 所以, 在实际中; mysql会自行选择:
要么使用 Index Nested-Loop Join, 要么使用 Block Nested-Loop Join;
这取决于join的两个表, 是大表还是小表, 有索引还是没有索引;
- 如果2个表join, 一个无索引, 一个有索引, 就使用无索引表作为驱动表, 内层嵌套循环表使用有索引的表(Index 循环嵌套算法);
- 如果2个表join, 都没有索引, 就使用小表作为驱动表, 大表作为内层循环嵌套表, 同时选用Block 嵌套循环算法;
3. 优化思路小结
1). 并发量太高时, 系统性能下降很快, 不要超过2个表join;
2). 复杂的join语句, 需要锁定的资源也更多, 阻塞的其他线程也更多;
3). 复杂的query语句, 拆分成多个简单的, 分步执行;
4). 实在不行, 加热点数据存 Redis等其他 NoSQL组件;
5). 只取出需要的列, 不要 select*
5.1) 取的越多, 传给客户端的越大, 浪费带宽;
5.2) 排序时输出列越多, 浪费内存越大(Using Filesort)
以 t2 (小表, 只有3列, 10行记录), select* 和select name:
mysql> explain select * from t2 order by name;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select name from t2 order by id;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select name from t2 order by name;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | NULL | name | 33 | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
前两个都使用了 filesort: 可以得出结论:
- 如果 order by 的字段没有索引, 排序会
Using filesort; - 如果select* 了, 即使order by的字段有索引, 也会
Using filesort; - 如果select的列和order by的列都有索引, 那么就只使用索引
Using index;
5.3) select* 改变执行计划
6). 当where条件可以使用的多个列都有索引时, 选择key_len最短的;
本质就是列的类型的长度(如果建索引没有指定长度的话), 比如 name varchar(100), key_len=103;
varchar另外加3个字节;
7). 尽可能在索引中完成排序-order by 字段加索引;
如果 order by 的字段没有索引, 需要再内存中开辟空间, 甚至还要生成临时文件落盘增加IO开销;
Using filesort
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 hi@niewj.com


